BACK TO Blog
BACK TO Blog
A Practical Guide to Different Types of Asset Maintenance
Published On April 15, 2025 | 5 Min Read
Why Maintenance Needs a Smarter Approach?
For any organization with physical assets, applying the right types of asset maintenance to keep things running is not optional, it is essential. Whether you manage factory lines, utilities, or facilities, the way equipment is maintained affects everything from costs to compliance.
Not every asset needs the same type of care. Some require routine checks, others need real-time data, and some just need quick fixes when they stop working. Choosing the right strategy can make a real difference in efficiency and budget.
This article breaks down the six key types of asset maintenance: preventive, predictive, reactive, condition-based, corrective, and reliability-centered maintenance. You will get practical insight into how they work and where they fit best.
Exploring the Six Core Types of Asset Maintenance
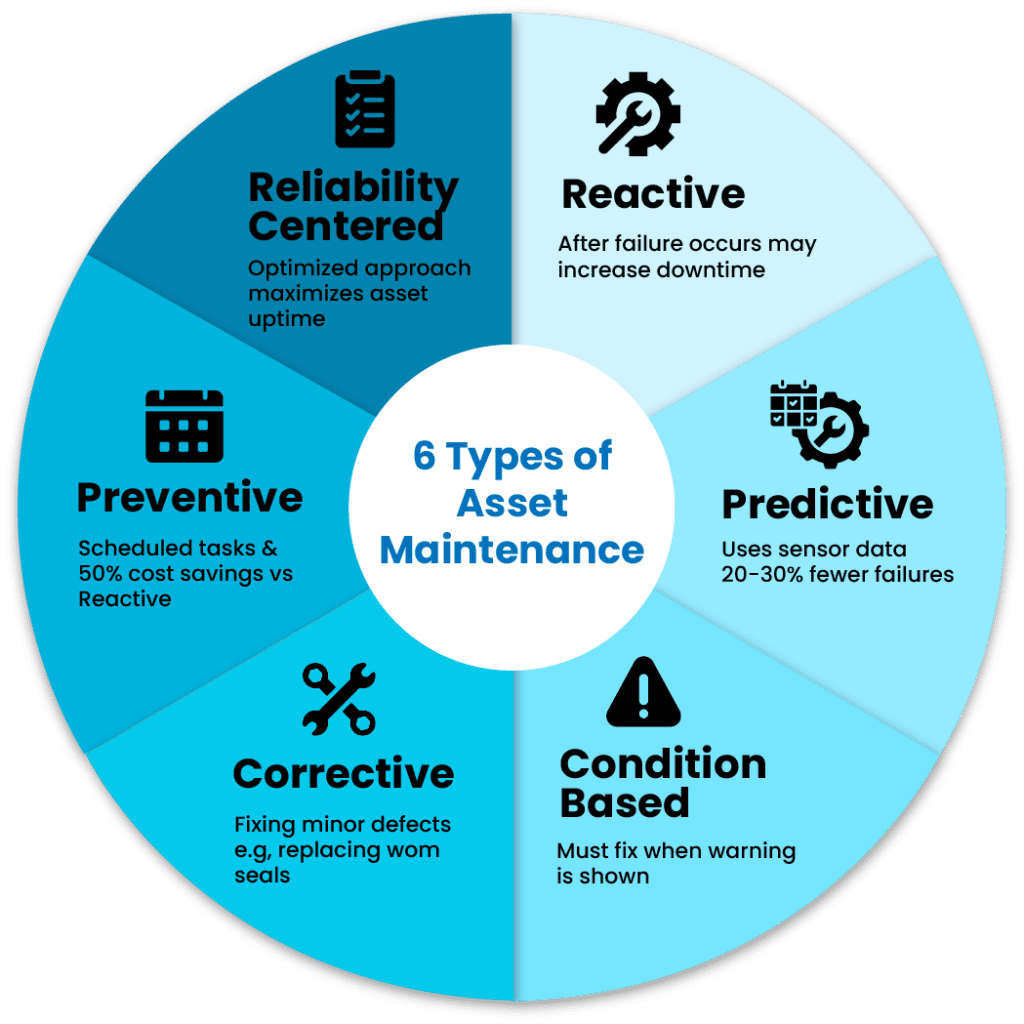
1. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach to asset maintenance management. It focuses on scheduled tasks such as cleaning, inspections, lubrication, or parts replacement regardless of an asset’s current condition. This maintenance strategy is a cornerstone of many industrial maintenance methods due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Preventive maintenance is performed on a regular schedule, regardless of whether the asset appears to need service. The objective is to keep everything running by staying ahead of failures.
Why it works:
- Helps reduce downtime by catching issues early
- Maintains compliance with safety regulations
- Supports long-term maintenance cost reduction
- Improves overall asset performance and reliability
Practical Use Cases:
- Quarterly checks on elevators or escalators
- Bi-monthly HVAC servicing for data centers
- Filter replacement in manufacturing every 500 hours of operation
By integrating preventive tasks into your maintenance plan, you create a consistent process that aligns with your equipment maintenance types and planning goals.
Example: A manufacturing facility performs quarterly elevator checks as part of its routine asset maintenance program. Even without reported issues, the team inspects cables, doors, and electrical systems to avoid unexpected failures.
According to Plant Engineering, companies that follow preventive maintenance schedules can see a 10-12% increase in asset efficiency.
This approach not only improves performance but also supports broader asset maintenance best practices across industries.
Ideal for: Operations where uptime is critical and compliance standards are high such as healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and heavy industry.
2. Reactive Maintenance
This approach is straightforward: wait until something stops working, then repair it. It sounds risky and often is but it still has a place for lower-cost or non-critical items.
Key Characteristics:
- Zero scheduling action is taken post-failure
- Useful for non-critical assets where downtime has limited consequences
- No upfront planning or monitoring required
Risks and Drawbacks:
- Higher downtime costs for key systems
- Emergency repair expenses can add up quickly
- Disruptions in workflow and supply chains
Examples in Action:
- Replacing light bulbs or signage only when they fail
- Repairing backup pumps or valves after breakdowns in a redundant system
Industry benchmarks suggest reactive maintenance can cost 3 to 5 times more than preventive approaches when applied to essential assets.
Ideal for: Low-priority equipment or facilities where redundancy exists, and unexpected breakdowns are acceptable.
Take the next step towards proactive asset careEmpower your asset maintenance team with strategies that reduce costs, improve uptime, and protect long-term performance using asset maintenance management software. |
3. Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Predictive maintenance takes a smarter route. It monitors equipment in real time and uses trends to spot trouble before it happens. It’s great for high-value or hard-to-replace machines.
Technological Enablers:
- Smart sensors that monitor vibration, temperature, pressure, and more
- Integration with Enterprise Asset Management systems (EAM)
- AI models that forecast failure based on historical data trends
Why Is It Strategic?
- Extends asset lifespan by acting only when necessary
- Minimizes labor hours spent on unnecessary inspections
- Avoids unnecessary part replacements
Examples:
- Detecting early misalignment in conveyor belts via vibration analytics
- Monitoring oil viscosity in generators to schedule replacements based on degradation not time alone
According to PwC, predictive maintenance can increase equipment uptime by 35–45% while reducing maintenance cost by nearly 20%.
Ideal for: Sectors like aviation, energy, and precision manufacturing where failure risks are high, and downtime is expensive.
4. Condition-based Maintenance (CBM)
Condition-based maintenance uses specific indicators of performance, such as temperature, fluid levels, or pressure changes to trigger intervention. It strikes a balance between preventive and predictive techniques.
How Does It Work?
- Assets are equipped with sensors or assessed through manual inspection
- Maintenance is performed only if thresholds are exceeded
- Systems trigger alerts when action is required
Advantages:
- More cost-effective than blanket preventive servicing
- Increases technician efficiency by avoiding false positives
- Reduces part waste and premature replacements
Use Case Examples:
- Servicing compressors when pressure drops below operational thresholds
- Changing lubrication in gearboxes when contamination levels rise
The condition-based maintenance approach is credited with reducing maintenance frequency by 15–20% in industrial settings while preserving asset health.
Ideal for: Equipment with variable workloads or environmental conditions where wear and tear patterns are not consistent.
5. Corrective Maintenance
This is not just about patching problems, it is about stopping them from coming back. Corrective maintenance kicks in when something breaks more than once or shows deeper design or usage flaws.
What Does It Involve?
- Identifying what caused the failure (e.g., poor installation, user error, or environmental conditions)
- Updating SOPs or retraining staff
- Modifying equipment or implementing design changes
Strategic Benefits:
- Helps eliminate recurring issues
- Encourages a culture of continuous improvement
- Enhances safety and quality across facilities
Example Scenarios:
- After a robotic arm fails due to repeated overload, torque limits are revised
- Frequent belt slips in a mixer lead to a pulley realignment and motor upgrade.
A study in Reliability Engineering notes that facilities using structured corrective approaches see a 12% increase in equipment availability year-over-year.
When to apply: When failure patterns emerge and quick fixes lead to repeated breakdowns or safety incidents.
6. Reliability-centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-centered maintenance is a structured decision-making process used to determine the most effective way to maintain a system based on risk and performance impact. Reliability-centered maintenance analyzes each asset’s function and the effect of failure, and then applies the right maintenance strategy accordingly.
Key Components:
- Asset prioritization based on business impact
- Risk analysis to determine failure consequences
- Selection of preventive, predictive, or reactive methods as needed
Why RCM Matters:
- Avoids under- or over-maintenance of assets
- Improves allocation of labor and inventory
- Aligns maintenance practices with organizational KPIs
Implementation Example:
- In a food processing facility, reliability-centered maintenance might prioritize real-time monitoring for refrigeration units while using simple PM for conveyor rollers.
- According to the Society for Maintenance & Reliability Professionals (SMRP), RCM adoption can improve overall asset utilization by 10–15% across enterprises.
Ideal for: Organizations with complex infrastructure and diverse asset criticality, such as logistics hubs, energy grids, and large-scale manufacturers.
Choosing Which Maintenance Type Works for You
Your business should not feel locked into using only one type of asset maintenance (like preventive or reactive). Instead, it is usually more effective to combine different strategies depending on the criticality of the equipment, cost implications, and operational needs. This flexible, tailored approach often delivers better performance and cost-efficiency across various types of assets.
In fact, most operations benefit from a blended approach based on:
- How critical the asset is
- How much downtime would cost
- What tools or staff you have
Which Maintenance Type Fits Your Needs?
| Maintenance Strategy | Ideal use case | Cost Profile | Tools and Resources |
| Preventive Maintenance | Routine service for high-use/safety-critical assets | Moderate, predictable | Calendars, logs, task schedules |
| Reactive Maintenance | Low-priority, replaceable equipment | High (due to unplanned downtime) | Minimal; repair kits |
| Predictive Maintenance | Assets where real-time performance is crucial | Higher initial, cost-saving long-term | Sensors, data analytics, AI tools |
| Condition-Based Maintenance | Equipment with measurable degradation indicators | Balanced | Threshold sensors, basic monitors |
| Corrective Maintenance | Equipment with repeated or root-cause issues | Moderate | Diagnostic tools, root cause analysis |
| Reliability-Centered Maintenance | Complex environments managing multiple asset types | Variable | Mixed approach; strategic planning tools |
Insights from Industry Leaders
“Our transition to condition-based maintenance let us focus attention where it mattered. The cost savings in labor alone were impressive.”
— Maria H., Operations Lead, Ecosystems Group
“Predictive tools gave us insights we never had before. Now we act early, not late—and that’s a big deal when every hour of downtime costs us.”
— James T., Facilities Director, PeakLine Services
“We replaced five reactive routines with two targeted preventive schedules. Our uptime is better and our budget is more predictable.”
— Sheila N., Maintenance Supervisor, Vector Assembly
Final Thoughts
Asset maintenance management is not just about reducing downtime it is about smarter resource use, better planning, and stronger asset life cycles. By choosing the right blend of equipment maintenance types, businesses can boost reliability, reduce repair costs, and improve safety across the board.
The most effective programs mix and match approaches depending on asset importance, operating conditions, and business goals.
Whether you are refining your existing plan or building a new one from scratch, focus on strategies that:
- Improve uptime
- Reduce emergency repairs
- Extend equipment life
- Support regulatory compliance
- Optimize team efficiency
Ready to Transform Your Maintenance Plan?If your team is still working from spreadsheets or reacting to failures as they happen, it is time to make a shift. Modern asset maintenance tools and frameworks can: 1. Streamline work order management 2. Improve maintenance planning and scheduling 3. Align maintenance tasks with real-time asset health 4. Cut costs and extend equipment life 👉 Ready to modernize your asset maintenance strategy? Book a consultation and explore how we can help. |