BACK TO Blog
BACK TO Blog
Asset Rental Management
Asset Maintenance
Best Preventive Maintenance Options for Assets
- May 12, 2025
- DreamzCMMS Team
- 10 minutes read

- May 12, 2025
- DreamzCMMS Team
- 10 minutes read
The sudden breakdown of equipment in asset-intensive settings disrupts operational activities while increasing costs and endangering safety. Businesses implement smart preventive maintenance options to extend asset life while reducing unplanned downtime and ensuring consistent performance.
The correct maintenance strategy which modern technology supports allows businesses that manage manufacturing facilities and healthcare centers and rental equipment operations to achieve significant performance improvements.
This blog discusses the main asset preventive maintenance strategies with an explanation of how preventive maintenance software and maintenance scheduling tools enhance the process.
Explore how Asset Maintenance Management Software from DreamzCMMS can help you automate maintenance tasks, reduce downtime, and optimize asset performance.
Understanding Preventive Maintenance
Regular inspections together with servicing and repairs form preventive maintenance which stops equipment failures from happening unexpectedly. The proactive approach of preventive maintenance differs from reactive maintenance since it focuses on continuous reliability rather than addressing problems after breakdowns.
The implementation of maintenance management software enables organizations to schedule automated services and maintain detailed service records and work orders that require less documentation for better team coordination. The transition from manual scheduling and reactive responses to proactive care allows maintenance teams to access valuable data insights and reduces operational disruptions.
The correct strategy enables organizations to enhance equipment maintenance planning while lowering repair expenses and supporting regulatory compliance and improving workforce productivity. The standardization of workflows across departments becomes possible when organizations implement this approach.
Top Preventive Maintenance Options to Consider
The following preventive maintenance strategies should be considered for implementation. Choosing the optimal preventive maintenance strategy requires knowledge of asset types and operational objectives together with usage patterns.
The following methods represent the most effective preventive maintenance strategies:
1. Time-Based Maintenance
Time-based maintenance stands as a basic yet common maintenance approach. The schedule for maintenance tasks follows predetermined periodic periods of weekly, monthly, or yearly intervals without regard to asset usage levels. This approach functions best for systems that are not critical since failures in these systems would not create major operational disruptions.
For example, replacing HVAC filters every three months or lubricating motors quarterly. The straightforward method can result in unnecessary maintenance activities, which cost more without generating significant added value.
A CMMS service interval tracking system enables automatic reminder generation which prevents task oversights. The consistent approach leads to enhanced safety and prompt actions.
2. Usage-Based Maintenance
The scheduling of maintenance happens through this approach after asset usage reaches defined levels such as operating hours, mileage or production cycles. The maintenance approach is better suited to asset conditions than calendar-based schedules because it matches operations to actual usage.
The implementation of usage-based maintenance works best for mobile equipment as well as vehicles and machinery that operate infrequently since it requires real-time tracking of asset usage. Asset usage tracking occurs through sensors and preventive maintenance software connections that monitor actual asset usage.
This strategy provides maximum advantage to transportation and utility and equipment rental operations because their assets experience wide-ranging usage levels.
3. Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
The scheduling of maintenance through condition-based maintenance depends on current asset data which determines optimal service times. Equipment condition gets monitored by using indicators which include temperature, vibration, oil analysis and performance metrics.
The system initiates maintenance only when thresholds are met, which avoids excessive and insufficient maintenance service. The initial expense of installing IoT sensors along with monitoring systems leads to substantial savings through longer uptime and lower costs from minimized unnecessary interventions.
The combination of a maintenance management system with RFID Asset Tracking Software provides enhanced accuracy in condition monitoring and speedier response to developing issues.
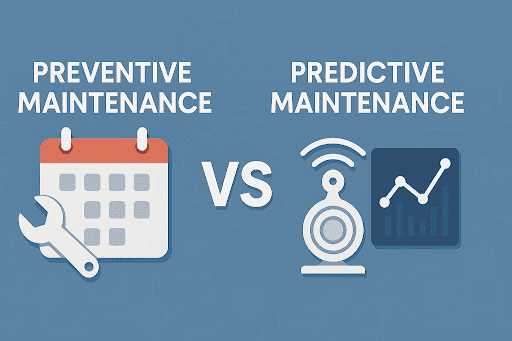
4. Predictive Maintenance
The forecasting of equipment failures happens through advanced analytics and AI models that analyze historical and real-time data. Organizations use performance trend analysis to predict equipment breakdowns which allows them to perform maintenance right before equipment failure occurs.
Predictive maintenance provides organizations with the ability to minimize unplanned downtime while reaching maximum asset performance levels. Predictive maintenance works best in high-value or safety-critical asset sectors although it needs advanced data infrastructure and specialized technical knowledge.
The success of this method depends on platforms that collect historical service records and asset performance data, particularly when failures result in significant consequences.
5. Failure-Finding Maintenance
The approach investigates hidden equipment breakdowns that become noticeable only during emergencies affecting safety-critical systems and backup components such as emergency lights and generators.
Scheduled simulations, along with tests, allow failure-finding maintenance to detect hidden failures that would only emerge during emergencies. The method requires scheduled inspections and tests to find hidden equipment breakdowns before they become active.
The method serves as a fundamental component of compliance approaches and achieves its best results when maintenance checklist automation supports thorough inspection and tracking. The method serves healthcare facilities and public infrastructure together with industrial safety systems for fulfilling stringent regulatory standards.
6. OEM-Based Preventive Maintenance
The maintenance recommendations provided by original equipment manufacturers allow you to keep your assets in a condition that follows proven standards. The method helps organizations meet warranty requirements and improve their asset operational effectiveness.
Preventive maintenance software users can integrate OEM-based schedules through customization options that consider usage patterns and site environment conditions. Over time, organizations may fine-tune OEM protocols to better fit their operations.
During asset ownership's initial period and warranty coverage, this approach remains the best choice. To understand how preventive care fits within the broader maintenance landscape, explore the various Types of Asset Maintenance that organizations implement across different asset classes and operational environments.
Selecting the Right Maintenance Strategy
Multiple factors determine the selection of an appropriate approach, which includes asset criticality and usage frequency, along with cost implications and technical capacity.
Begin by determining which operational assets require the most attention. Each asset requires evaluation of its potential downtime effect, together with failure cost calculations. Predictive or condition-based maintenance becomes suitable for assets that operate frequently and have essential mission functions. Time-based and OEM-recommended care should be enough for less complex assets.
Your existing systems also matter. Organizations that use CMMS systems and have started their digital transformation journey find it simpler to implement advanced asset preventive care solutions at scale. The combination of strategy with capability leads to sustainable implementation.
Building a Scalable Preventive Maintenance Culture
A successful preventive maintenance strategy serves as only one aspect of the complete solution. The development of an asset reliability culture and continuous improvement philosophy demands equal emphasis. The key to successful maintenance optimization exists in adopting a proactive approach combined with employee training and KPI alignment between maintenance goals and corporate objectives.
Leadership functions as the primary force which determines expectations while providing essential resources for sustaining long-term success. Maintenance personnel require knowledge about their responsibilities but also need to understand preventive care's role in maintaining business profitability as well as safety and customer satisfaction.
The implementation of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) together with checklists and work order tracking within maintenance management systems helps organizations maintain performance visibility and accountability. Through mobile apps designed for maintenance teams employees can perform independent work while accessing real-time data and receiving immediate maintenance task notifications.
The Role of Maintenance Software and Scheduling Tools
Today's preventive maintenance approaches succeed through automated systems which provide immediate data access. Preventive maintenance software functions as the core component to handle tasks and schedules as well as team management and performance indicator tracking. The system optimizes all aspects of asset care beginning with inspections and repairs and parts ordering and reporting.
The platforms work optimally with maintenance scheduling tools to provide the following features:
- Automate recurring service tasks
- Assign work orders to available technicians
- Track real-time job status and delays
- Enable compliance documentation
- Send maintenance task alerts
An integration of Field Service Management Software with mobile maintenance team applications provides enhanced communication speed and job transparency and improves technician responsibility especially when operating across different locations.
The tools provide improved reporting functionality that enables maintenance managers to evaluate performance data and detect patterns while planning enhancements.
Real-World Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Options
Organizations implementing structured preventive maintenance strategies achieve better uptime alongside improved safety performance and cost management.
Rental companies implementing Asset Rental Management Software implement usage-based and predictive maintenance strategies for equipment downtime prevention while maximizing asset availability. Manufacturing facilities depend on condition-based triggers to stop equipment failures. Facility managers utilize time-based schedules integrated with Facility Management Software to handle various buildings and service contractors effectively. These proactive approaches align with broader strategies for maximizing asset performance, as discussed in our detailed guide on the Benefits of Asset Management.
Preventive strategies also help in aligning with audit requirements, reducing regulatory risks, and planning inventory more effectively. Maintenance managers gain deeper control over budgets, parts usage, and workforce scheduling, all while maintaining a safer work environment.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Preventive maintenance adoption does not come without facing certain challenges. The main challenges include disparate data, worker resistance, and inconsistent standards.
To overcome these:
- Digitize your asset registry and service logs
- Automate service interval tracking and work order flows
- Centralize information in a unified maintenance management system
- Train your team using mobile-first solutions that simplify tasks
Starting with a pilot on your most critical assets is a great way to build momentum and demonstrate ROI. This phased approach allows teams to refine processes and develop champions internally.
Organizations should also work on continuous improvement by evaluating metrics such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR).
Future Trends in Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is evolving. The combination of Industry 4.0 with smart facilities has driven maintenance operations to become more data-oriented and automated.
Emerging trends include:
- AI-generated service recommendations
- Maintenance decision support via digital twins
- Remote monitoring and diagnosis
- Mobile-first execution and technician dashboards
- Fully automated maintenance checklist automation
Businesses will be able to transition from scheduled maintenance to condition-aware and self-adjusting maintenance programs as these technologies become more mature. Predictive insights and data visualizations will empower teams to make faster, smarter decisions and create value beyond traditional operations.
Industry Use Cases and Cross-Sector Value
Each industry faces unique challenges, but preventive maintenance delivers measurable results across the board. For instance, condition-based monitoring of diagnostic equipment in the healthcare industry ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance. Predictive analytics in manufacturing operations helps reduce production delays and decrease scrap rates.
In the logistics sector, usage-based maintenance of delivery fleets minimizes delays and enhances asset utilization. Asset Rental Management Software users report that faster turnaround times and fewer customer complaints occur when assets are proactively serviced between rentals.
Meanwhile, facilities powered by Facility Management Software benefit from structured equipment maintenance planning, automated checklist routines, and integrated vendor coordination all crucial for managing multiple buildings or locations efficiently.
Conclusion
The path to high-performing, resilient operations begins with the right preventive maintenance options. Whether you start with time-based schedules or aim for predictive intelligence, consistency, visibility, and scalability are key.
By using preventive maintenance software, maintenance scheduling tools, and centralized maintenance management systems, businesses can boost equipment reliability, improve compliance, and master asset performance.
Discover how DreamzCMMS can assist you in developing a personalized, intelligent preventive maintenance program that meets your objectives.
- Looking for a complete solution to modernize your maintenance operations?
- Are you seeking an entire solution to modernize your maintenance operations?
DreamzCMMS helps businesses simplify their complex maintenance workflows and enhance asset visibility and automate preventive care across their facilities.
Ready to experience the benefits firsthand?Schedule a Free Demo today and see how our powerful Asset Maintenance Management Software helps you reduce downtime, ensure compliance, and extend the life of your critical equipment. |
Ready for More?
Talk to one of our CMMS experts and see how DreamzCMMS can simplify your maintenance operations.
Book a free consultation